Why is it important to know how to convert between RMS and Peak to Peak voltages?
- RMS voltage is used to calculate power for AC circuits.
$$P_{watts(W)}=V_{(rms)}\times I_{amps(rms)}$$
$$P_{watts(W)}=\frac{V_{rms}^2}{R_{ohms(\Omega)}}$$
- Our Oscilloscope displays Peak to Peak voltage.
- Both averaging and true-RMS DMMs display the RMS voltage of sinusoidal waveforms. For more information FLUKE true-RMS DMMs.
Converting Oscilloscope Peak to Peak voltage to RMS voltage:
- Divide Peak to Peak voltage by two.
$$v_{p}=\frac{v_{pp}}{2}$$
- Find the RMS voltage.
$$V_{rms}=\frac{v_{p}}{\sqrt{2}}$$
$$V_{rms}={v_{p}\times0.707}$$
Converting RMS voltage to Peak to Peak voltage:
- Find Peak voltage.
$$v_{p}=V_{rms}\times\sqrt{2}$$
$$v_{p}=\frac{V_{rms}}{0.707}$$
- Find the Peak to Peak voltage.
$$v_{pp}={v_{p}\times2}$$
What voltage peak to peak would you expect to measure with an oscilloscope when measuring 120Vrms?
Converting RMS Voltage to Peak to Peak Voltage.
- Find Peak voltage.
$$v_{p}=120V_{rms}\times\sqrt{2}$$
$$v_{p}=\frac{120V_{rms}}{0.707}$$
$$v_{p}=169.7v_{p}$$
- Find the Peak to Peak voltage.
$$v_{pp}={v_{p}\times2}$$
$$v_{pp}={169.7v_{p}\times2}$$
$$v_{pp}=339.4v_{pp}$$
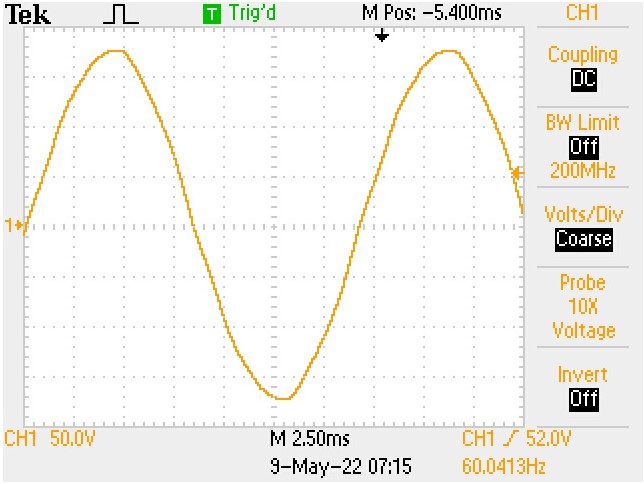
Try measuring the image waveform of this post.
- Notice CH1 is on 50V/division.
- Count the number of major and minor divisions Peak to Peak.
- Each minor division is equal to 0.2 divisions.
- Multiply the 50V/division by the number of divisions to get Peak to Peak voltage.
- Finally, Convert to RMS voltage.